Early this morning, security researcher Derek Knight discovered a new Locky campaign spewing out emails that pretend to be an ISP complaint stating that SPAM has been detected coming from the computer. After testing the installation of Locky from this new campaign, MalwareHunterTeam discovered that Locky had also changed the extension for encrypted files to .AESIR. This new extension continues to stay within the Norse god mythology, with the previous variant using the Thor extension.
Unfortunately, at this time there is still no way to decrypt the Locky Ransomware.
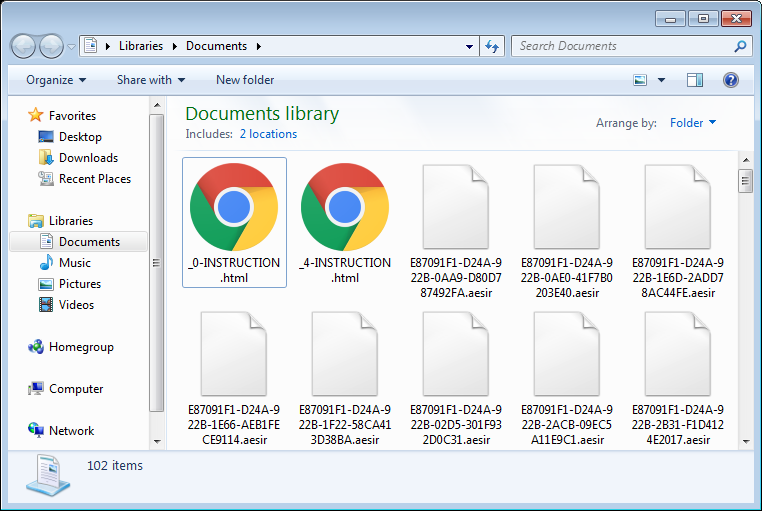
Locky AESIR variant being distributed via Fake ISP Complaint Emails
This new Locky campaign is being distributed through emails that pretend to be a complaint from your ISP, which state that SPAM is being sent from your computer. These emails will contain a subject of Spam mailout and contain a zip attachment with a name like logs_[target_name].zip. Inside this ZIP file is a JS file that when opened will download and execute the Locky ransomware.
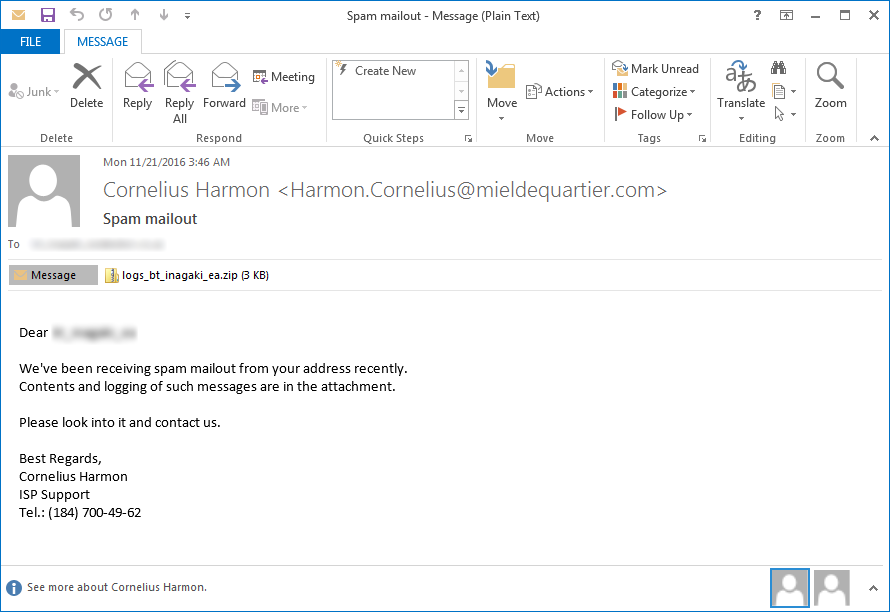
Locky continues to be installed via DLL Files
When the JS attachment is executed it will download an encrypted DLL and decrypt it into the %Temp% folder of the machine. This DLL file will then be executed using the legitimate Windows program called Rundll32.exe in order to install Locky on the computer.
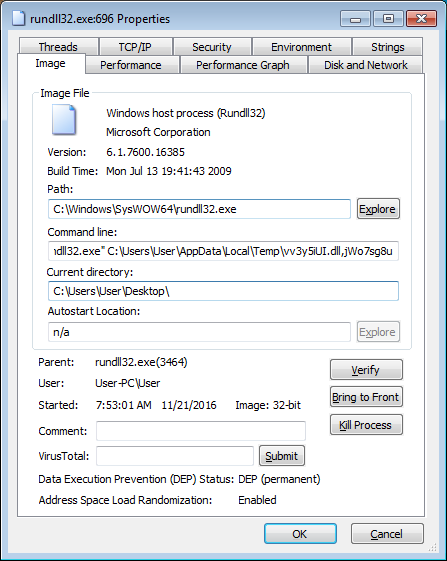
The Locky DLL is currently being executed with a command similar to the one below. Please note that the DLL export being used to install Locky will not be same in all cases.
"C:\Windows\System32\rundll32.exe" %Temp%\vv3y5iUI.dll,jWo7sg8u
Once Locky is installed it will scan the computer for certain file types and encrypt them. When encrypting a file, it will scramble the name and append the .aesir exension. For example, a file called test.jpg could be renamed to 016CCB88-61B1-ACB8-8FFA-86088F811BFA.aesir. The format for this naming scheme is first_8_hexadecimal_chars_of_id]-[next_4_hexadecimal_chars_of_id]-[next_4_hexadecimal_chars_of_id]-[4_hexadecimal_chars]-[12_hexadecimal_chars].aesir
The currently targeted extensions as per MalwareHunterTeam are:
.yuv, .ycbcra, .xis, .x3f, .x11, .wpd, .tex, .sxg, .stx, .st8, .st5, .srw, .srf, .sr2, .sqlitedb, .sqlite3, .sqlite, .sdf, .sda, .sd0, .s3db, .rwz, .rwl, .rdb, .rat, .raf, .qby, .qbx, .qbw, .qbr, .qba, .py, .psafe3, .plc, .plus_muhd, .pdd, .p7c, .p7b, .oth, .orf, .odm, .odf, .nyf, .nxl, .nx2, .nwb, .ns4, .ns3, .ns2, .nrw, .nop, .nk2, .nef, .ndd, .myd, .mrw, .moneywell, .mny, .mmw, .mfw, .mef, .mdc, .lua, .kpdx, .kdc, .kdbx, .kc2, .jpe, .incpas, .iiq, .ibz, .ibank, .hbk, .gry, .grey, .gray, .fhd, .fh, .ffd, .exf, .erf, .erbsql, .eml, .dxg, .drf, .dng, .dgc, .des, .der, .ddrw, .ddoc, .dcs, .dc2, .db_journal, .csl, .csh, .crw, .craw, .cib, .ce2, .ce1, .cdrw, .cdr6, .cdr5, .cdr4, .cdr3, .bpw, .bgt, .bdb, .bay, .bank, .backupdb, .backup, .back, .awg, .apj, .ait, .agdl, .ads, .adb, .acr, .ach, .accdt, .accdr, .accde, .ab4, .3pr, .3fr, .vmxf, .vmsd, .vhdx, .vhd, .vbox, .stm, .st7, .rvt, .qcow, .qed, .pif, .pdb, .pab, .ost, .ogg, .nvram, .ndf, .m4p, .m2ts, .log, .hpp, .hdd, .groups, .flvv, .edb, .dit, .dat, .cmt, .bin, .aiff, .xlk, .wad, .tlg, .st6, .st4, .say, .sas7bdat, .qbm, .qbb, .ptx, .pfx, .pef, .pat, .oil, .odc, .nsh, .nsg, .nsf, .nsd, .nd, .mos, .indd, .iif, .fpx, .fff, .fdb, .dtd, .design, .ddd, .dcr, .dac, .cr2, .cdx, .cdf, .blend, .bkp, .al, .adp, .act, .xlr, .xlam, .xla, .wps, .tga, .rw2, .r3d, .pspimage, .ps, .pct, .pcd, .m4v, .fxg, .flac, .eps, .dxb, .drw, .dot, .db3, .cpi, .cls, .cdr, .arw, .ai, .aac, .thm, .srt, .save, .safe, .rm, .pwm, .pages, .obj, .mlb, .md, .mbx, .lit, .laccdb, .kwm, .idx, .html, .flf, .dxf, .dwg, .dds, .csv, .css, .config, .cfg, .cer, .asx, .aspx, .aoi, .accdb, .7zip, .1cd, .xls, .wab, .rtf, .prf, .ppt, .oab, .msg, .mapimail, .jnt, .doc, .dbx, .contact, .n64, .m4a, .m4u, .m3u, .mid, .wma, .flv, .3g2, .mkv, .3gp, .mp4, .mov, .avi, .asf, .mpeg, .vob, .mpg, .wmv, .fla, .swf, .wav, .mp3, .qcow2, .vdi, .vmdk, .vmx, .wallet, .upk, .sav, .re4, .ltx, .litesql, .litemod, .lbf, .iwi, .forge, .das, .d3dbsp, .bsa, .bik, .asset, .apk, .gpg, .aes, .ARC, .PAQ, .tar.bz2, .tbk, .bak, .tar, .tgz, .gz, .7z, .rar, .zip, .djv, .djvu, .svg, .bmp, .png, .gif, .raw, .cgm, .jpeg, .jpg, .tif, .tiff, .NEF, .psd, .cmd, .bat, .sh, .class, .jar, .java, .rb, .asp, .cs, .brd, .sch, .dch, .dip, .pl, .vbs, .vb, .js, .asm, .pas, .cpp, .php, .ldf, .mdf, .ibd, .MYI, .MYD, .frm, .odb, .dbf, .db, .mdb, .sql, .SQLITEDB, .SQLITE3, .011, .010, .009, .008, .007, .006, .005, .004, .003, .002, .001, .pst, .onetoc2, .asc, .lay6, .lay, .ms11 (Security copy), .ms11, .sldm, .sldx, .ppsm, .ppsx, .ppam, .docb, .mml, .sxm, .otg, .odg, .uop, .potx, .potm, .pptx, .pptm, .std, .sxd, .pot, .pps, .sti, .sxi, .otp, .odp, .wb2, .123, .wks, .wk1, .xltx, .xltm, .xlsx, .xlsm, .xlsb, .slk, .xlw, .xlt, .xlm, .xlc, .dif, .stc, .sxc, .ots, .ods, .hwp, .602, .dotm, .dotx, .docm, .docx, .DOT, .3dm, .max, .3ds, .xml, .txt, .CSV, .uot, .RTF, .pdf, .XLS, .PPT, .stw, .sxw, .ott, .odt, .DOC, .pem, .p12, .csr, .crt, .key
When the encryption is done it will display ransom notes that provide information on how to pay the ransom. The names of these ransom notes have changed for the AESIR Locky variant and are now named _[number]-INSTRUCTION.html
-INSTRUCTION.html, and -INSTRUCTION.bmp.
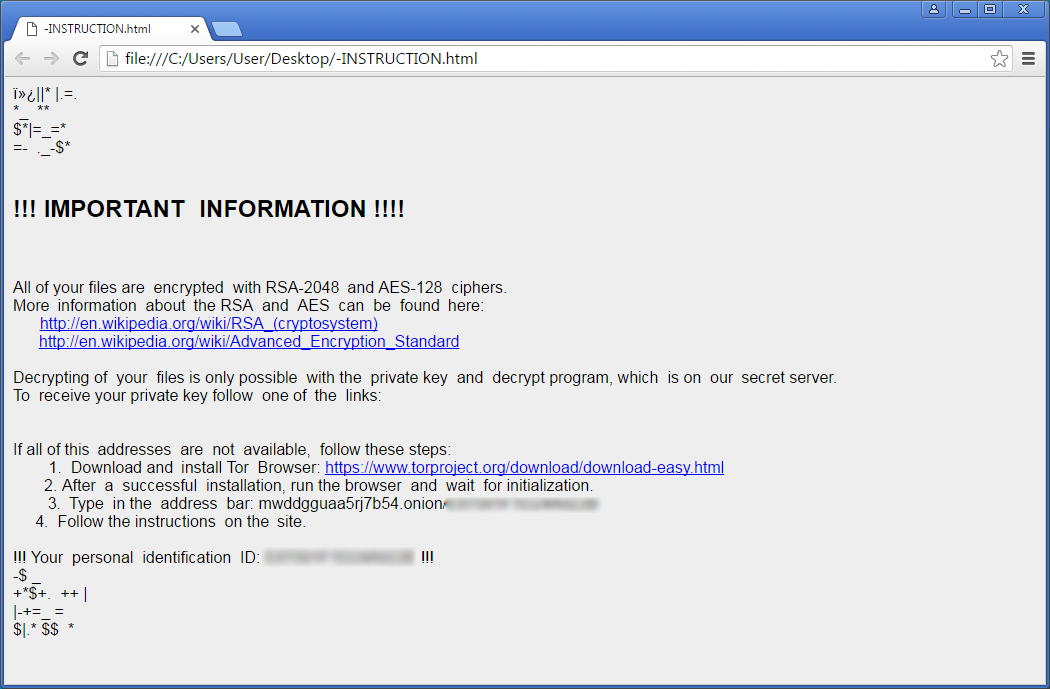
It is not possible to decrypt the Locky Ransomware AESIR Variant
Unfortunately, it is still not possible to decrypt files encrypted by the Locky Ransomware for free.
The only way to recover encrypted files is via a backup, or if you are incredibly lucky, through Shadow Volume Copies. Though Locky does attempt to remove Shadow Volume Copies, in rare cases ransomware infections fail to do so for whatever reason. Due to this, if you do not have a viable backup, I always suggest people try as a last resort to restore encrypted files from Shadow Volume Copies as well.









Comments
sandeep0315 - 7 years ago
how to deal with Ransom wares?
Lawrence Abrams - 7 years ago
Not sure I understand the question.
GuinnessStout - 7 years ago
Thanks for the awesome updates you provide. Do we know any of the IP's or domains this JS script is communicating to download the DLL?
Lawrence Abrams - 7 years ago
Those change often so do not have those. The C2 servers for this sample were 85.143.212.23,185.82.217.29,107.181.174.34.
oxfordfree - 7 years ago
Im doomed! :( All my files were encrypted. :(
woody188 - 7 years ago
FYI, ran into a .zzzzz Locky 12/2/2016 and they are now using random file names for the DLL but it is still a DLL, just not a DLL extension.
File: ultpkV.343
Size: 196608
MD5: 0BCC2B239182C73FCE76C930454596AC
Compiled: Wed, Nov 30 2016, 15:50:44 - 32 Bit DLL
Scan Date: 2016-12-02 10:48:13
Detections: 41/56