
A proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for a Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager authentication bypass flaw tracked as CVE-2024-29849 is now publicly available, making it urgent that admins apply the latest security updates.
Veeam Backup Enterprise Manager (VBEM) is a web-based platform for managing Veeam Backup & Replication installations via a web console. It helps control backup jobs and perform restoration operations across an organization's backup infrastructure and large-scale deployments.
Veeam issued a security bulletin about the critical flaw on May 21, warning about a critical vulnerability enabling remote unauthenticated attackers to log in to VBEM's web interface as any user.
The vendor urged its customers to address the problem by upgrading to VBEM version 12.1.2.172, while also sharing mitigation tips for those unable to apply the update immediately.
Exploit details
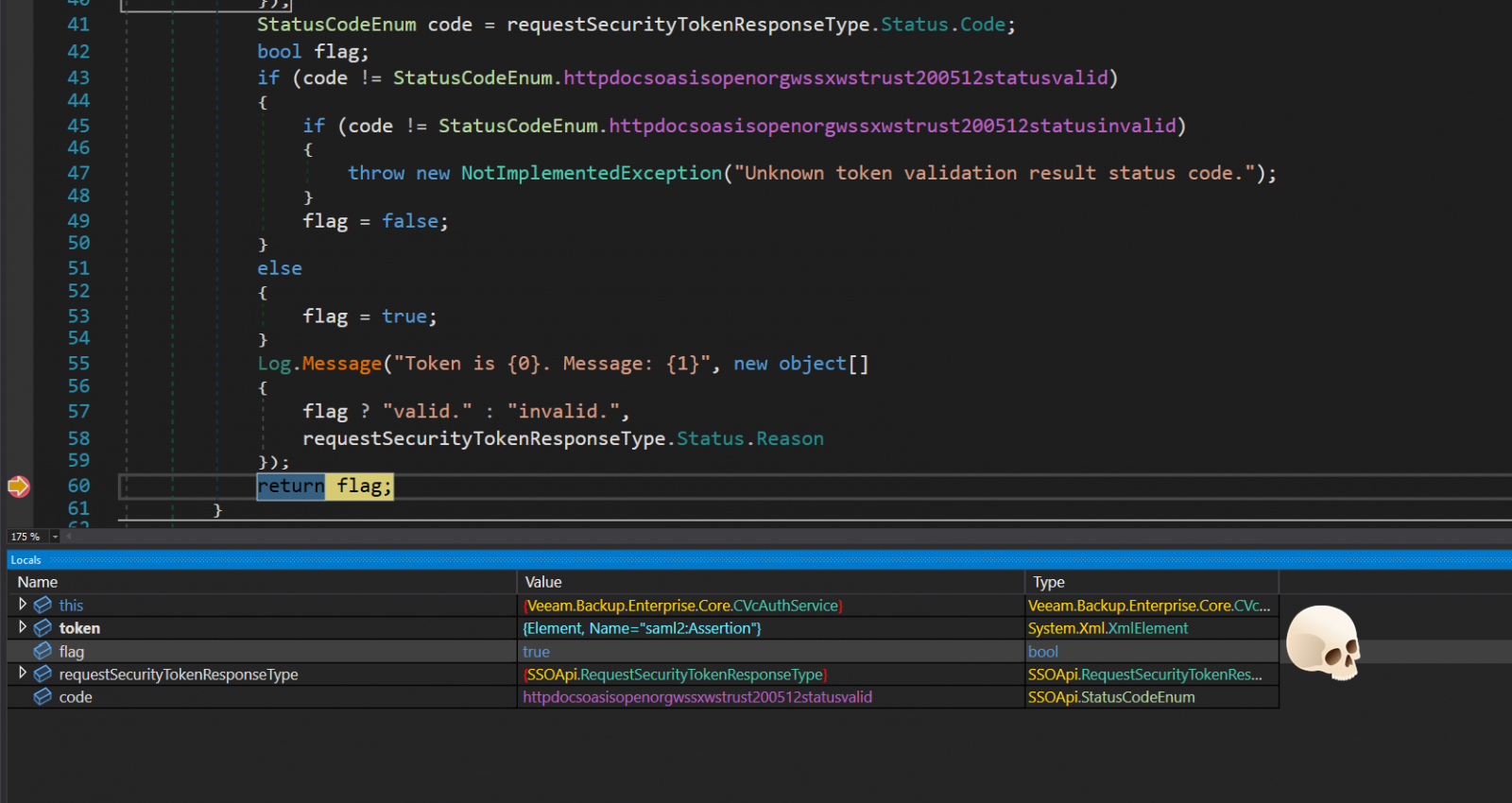
In a technical writeup by Sina Kheirkha, the cybersecurity researcher explains that the flaw lies in the 'Veeam.Backup.Enterprise.RestAPIService.exe' service, which listens on TCP port 9398, functioning as a REST API server for the main web application.
The exploit involves sending a specially crafted VMware single-sign-on (SSO) token to the vulnerable service using the Veeam API.
The token contains an authentication request that impersonates an administrator user and an SSO service URL that Veeam, crucially, doesn't verify.
The base64-encoded SSO token is decoded and interpreted in XML form to verify its validity via a SOAP request to an attacker-controlled URL.
This rogue server set up by the attacker responds positively to validation requests, so Veeam accepts the authentication request and gives administrator access to the attacker.
Source: summoning.team
The provided exploit demonstrates all the steps to exploit the vulnerability, including setting up a callback server, sending the crafted token, and retrieving a list of file servers as proof of successful exploitation.
Addressing the risks
Although no in-the-wild exploitation of CVE-2024-29849 has been reported yet, the public availability of a working exploit could change this in a short time. Therefore, updating to version 12.1.2.172 or later as soon as possible is critical.
Those unable to patch should follow these recommendations:
- Limit access to the VBEM web interface by restricting network access to only trusted IP addresses.
- Implement firewall rules to block unauthorized access to the ports used by Veeam services (e.g., port 9398 for the REST API).
- Enable multi-factor authentication for all accounts accessing VBEM.
- Deploy a Web Application Firewall to help detect and block malicious requests targeting VBEM.
- Regularly monitor and audit access logs for any suspicious or unauthorized access attempts, and set up alerts for login attempts from untrusted IP addresses.
- Isolate the VBEM server from other critical systems within your network to contain lateral movement risk.









Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now